Frequently Asked Questions
The most effective pharmacological treatments for postoperative pain management in orthopedic surgery patients typically involve a multimodal analgesia approach, which may include opioids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and adjuvant medications. Opioids such as morphine or hydromorphone are often utilized to provide potent analgesia for moderate to severe pain following procedures like total joint arthroplasty or fracture fixation. NSAIDs, including ketorolac and ibuprofen, play a crucial role in mitigating inflammatory responses while reducing the need for higher opioid doses, thereby minimizing potential side effects like respiratory depression or constipation. Additionally, regional anesthesia techniques such as nerve blocks can significantly enhance pain control when combined with systemic medications; these might include gabapentinoids like pregabalin or topical agents that address neuropathic components of postoperative pain. The integration of acetaminophen also contributes synergistically to overall analgesic efficacy while maintaining safety profiles across various patient populations undergoing orthopedic interventions.
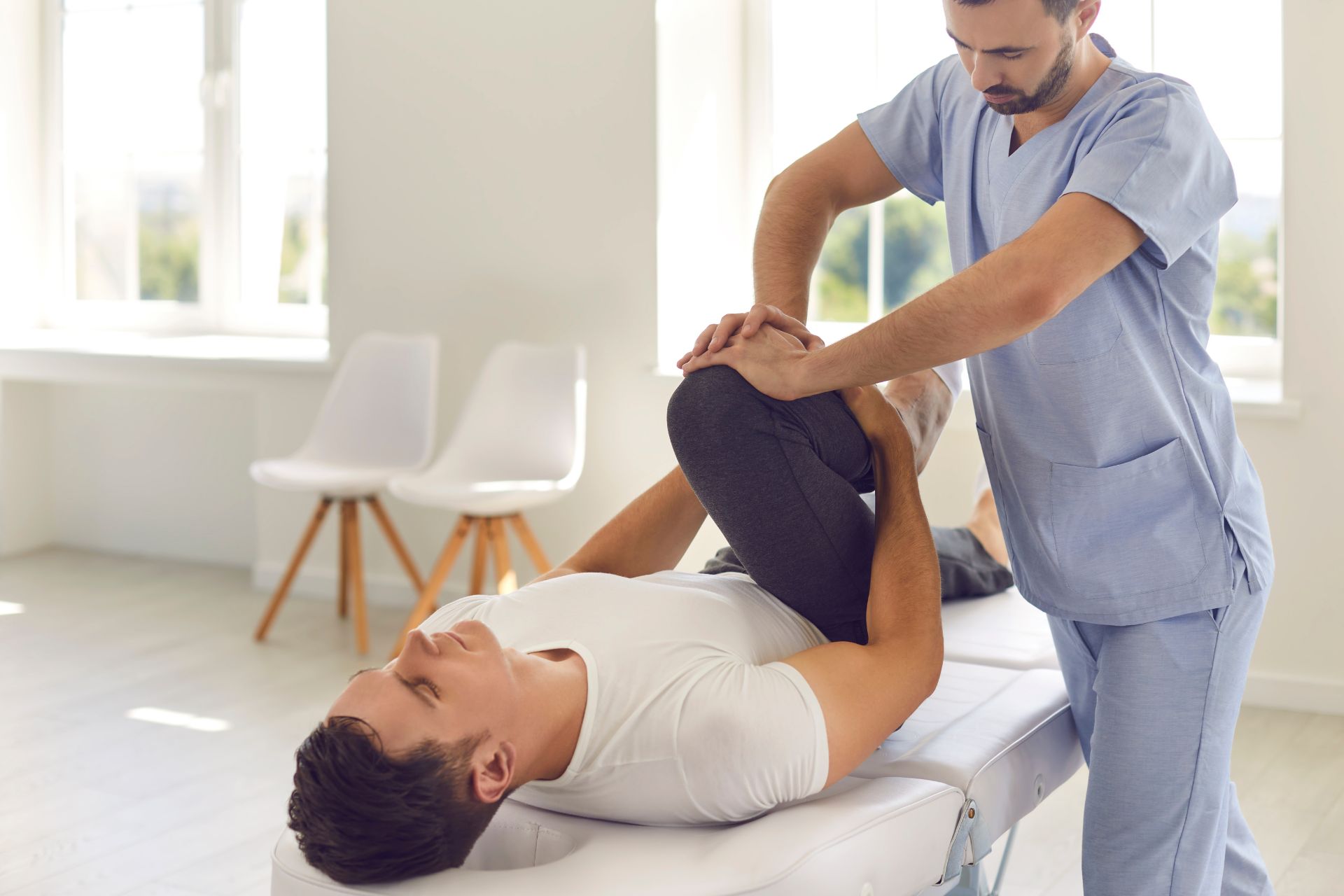
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in pain relief and functional recovery after total knee replacement surgery by employing targeted rehabilitation techniques that promote mobility, strength, and joint stability. Through personalized exercise regimens including range of motion exercises, strengthening routines for the quadriceps and hamstrings, as well as gait training to enhance ambulation mechanics, physical therapists facilitate optimal healing postoperatively. Additionally, modalities such as electrical stimulation and cryotherapy may be utilized to alleviate swelling and discomfort while promoting tissue repair. The therapist's expertise in manual therapy techniques helps address soft tissue restrictions around the knee joint, further aiding in restoring function. Overall, adherence to a structured physical therapy program significantly contributes to improved outcomes such as enhanced flexibility, reduced pain perception during activities of daily living (ADLs), increased endurance for prolonged weight-bearing tasks, and overall patient satisfaction with their surgical results.
Multimodal analgesia strategies play a crucial role in mitigating opioid consumption among hip fracture patients by employing an integrative approach that combines various pharmacological and non-pharmacological modalities to achieve optimal pain control. By utilizing agents such as acetaminophen, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), regional anesthesia techniques like nerve blocks, adjuvant medications such as gabapentinoids or corticosteroids, and complementary therapies like physical therapy or cognitive behavioral interventions, these strategies can significantly reduce the reliance on opioids for pain management. This comprehensive method not only addresses the multifaceted nature of postoperative pain but also minimizes opioid-related side effects including sedation, nausea, and constipation while enhancing patient satisfaction and functional recovery outcomes. Consequently, implementing multimodal analgesia effectively decreases overall opioid dosage requirements during hospitalization and post-discharge periods for individuals suffering from hip fractures.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can significantly assist orthopedic patients in managing chronic pain following joint surgeries by equipping them with effective coping strategies and altering maladaptive thought patterns related to their pain experience. Through techniques such as cognitive restructuring, mindfulness training, and relaxation exercises, CBT helps individuals reframe negative beliefs about their recovery process while enhancing self-efficacy and resilience. By addressing psychosocial factors that contribute to the perception of pain—such as anxiety, depression, and fear avoidance—CBT fosters better emotional regulation and promotes adaptive behaviors like physical activity adherence post-surgery. Furthermore, it may facilitate improved communication with healthcare providers regarding pain management plans, enabling a more holistic approach that integrates psychological support alongside traditional medical interventions for optimal rehabilitation outcomes.
Numerous studies provide compelling evidence supporting the efficacy of acupuncture as a complementary treatment for musculoskeletal pain in orthopedic settings, particularly for conditions such as osteoarthritis, lower back pain, and neck pain. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses highlight significant reductions in reported pain levels and improvements in functional mobility among patients receiving acupuncture alongside standard physical therapy interventions. The neurophysiological mechanisms underlying these benefits include the modulation of nociceptive pathways via endorphin release and improved local blood circulation at acupoints associated with specific anatomical sites of discomfort. Furthermore, randomized controlled trials demonstrate that acupuncture can enhance recovery rates post-surgery by alleviating inflammation and promoting tissue healing through biochemical mediators like cytokines. Overall, integrating acupuncture into conventional orthopedic care protocols may optimize patient outcomes while minimizing reliance on pharmacological analgesics such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).